Introduction
Pneumoperitoneum refers to the presence of free air in the abdominal cavity. Accompanied with the clinical presentation of acute abdominal pain, pneumoperitoneum found on imaging is highly suggestive of a perforated viscus. Urgent surgical evaluation and intervention is required to reduce patient morbidity and mortality as delayed treatment can lead to septic shock and multi-organ failure, eventually resulting in death.
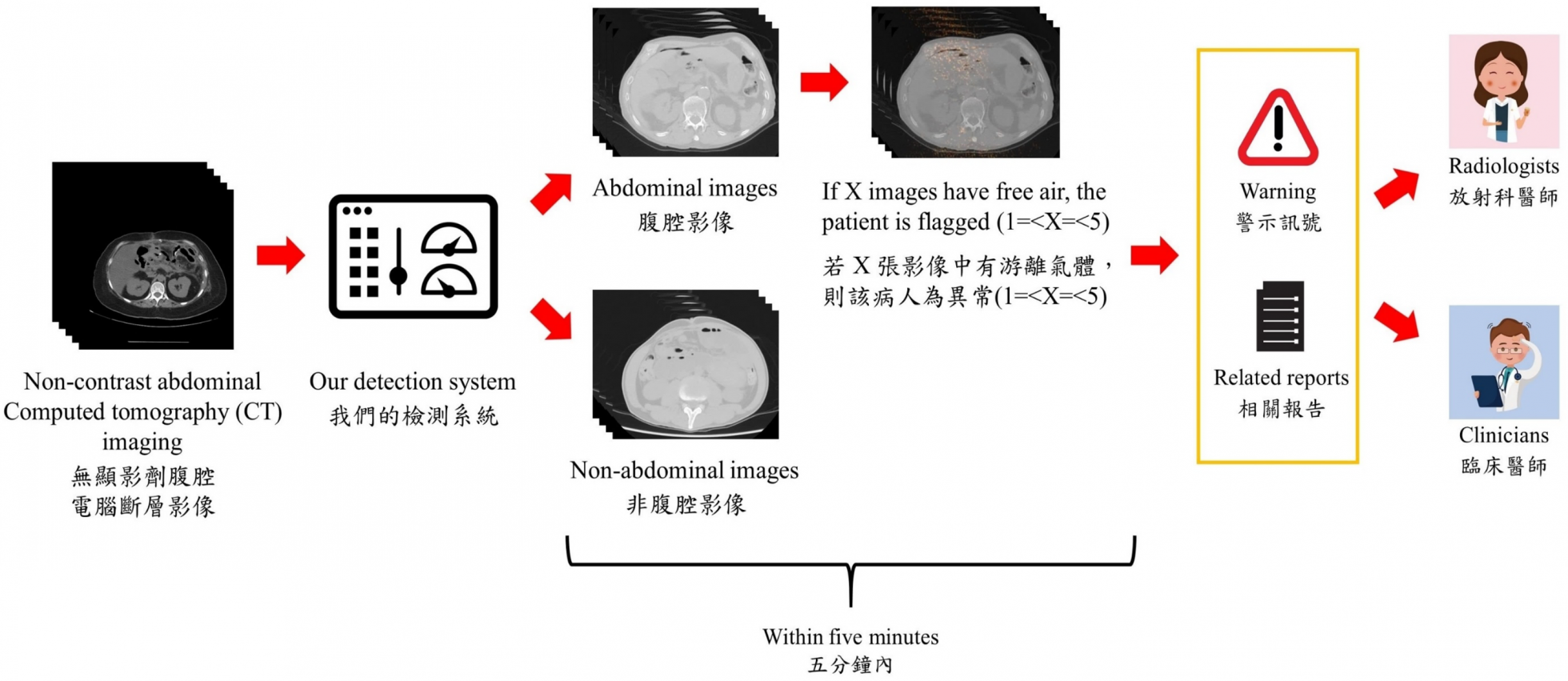
Computed tomography (CT) is the best imaging modality in identifying pneumoperitoneum. At present, response time to patients with pneumoperitoneum is heavily dependent on the vigilance of attending clinicians and turnaround reporting times of radiologists. This is however easily confounded by congested emergency departments with long lists of imaging due for reporting in addition to physician fatigue, amongst other factors.
We therefore embarked on the development of an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm via deep-learning to assist clinicians in the preliminary interpretation of CT abdominal imaging. Upon completion of CT scans, the images are automatically uploaded into our AI algorithm for the screening of abnormal free gas in the abdominal cavity. The process takes 5 minutes, and those with positive findings are immediately alerted to the on-site radiologists and/or physicians for further confirmation.
Our deep learning-powered novel algorithm and system thus assist with the rapid identification of pneumoperitoneum on abdominal CT imaging, with the ultimate aim of hastening the subsequent surgical evaluation and intervention required by these patients for better clinical outcomes.
Features / strengths
Pneumoperitoneum refers to the presence of free air in the abdominal cavity. Accompanied with the clinical presentation of acute abdominal pain, pneumoperitoneum found on imaging is highly suggestive of a perforated viscus. Urgent surgical evaluation and intervention is required to reduce patient morbidity and mortality as delayed treatment can lead to septic shock and multi-organ failure, eventually resulting in death.
Computed tomography (CT) is the best imaging modality in identifying pneumoperitoneum. At present, response time to patients with pneumoperitoneum is heavily dependent on the vigilance of attending clinicians and turnaround reporting times of radiologists. This is however easily confounded by congested emergency departments with long lists of imaging due for reporting in addition to physician fatigue, amongst other factors.
We therefore embarked on the development of an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm via deep-learning to assist clinicians in the preliminary interpretation of CT abdominal imaging. Upon completion of CT scans, the images are automatically uploaded into our AI algorithm for the screening of abnormal free gas in the abdominal cavity. The process takes 5 minutes, and those with positive findings are immediately alerted to the on-site radiologists and/or physicians for further confirmation.
Our deep learning-powered novel algorithm and system thus assist with the rapid identification of pneumoperitoneum on abdominal CT imaging, with the ultimate aim of hastening the subsequent surgical evaluation and intervention required by these patients for better clinical outcomes.
Specification in detail
Intellectual Property Office, MOEA
I801273