Introduction
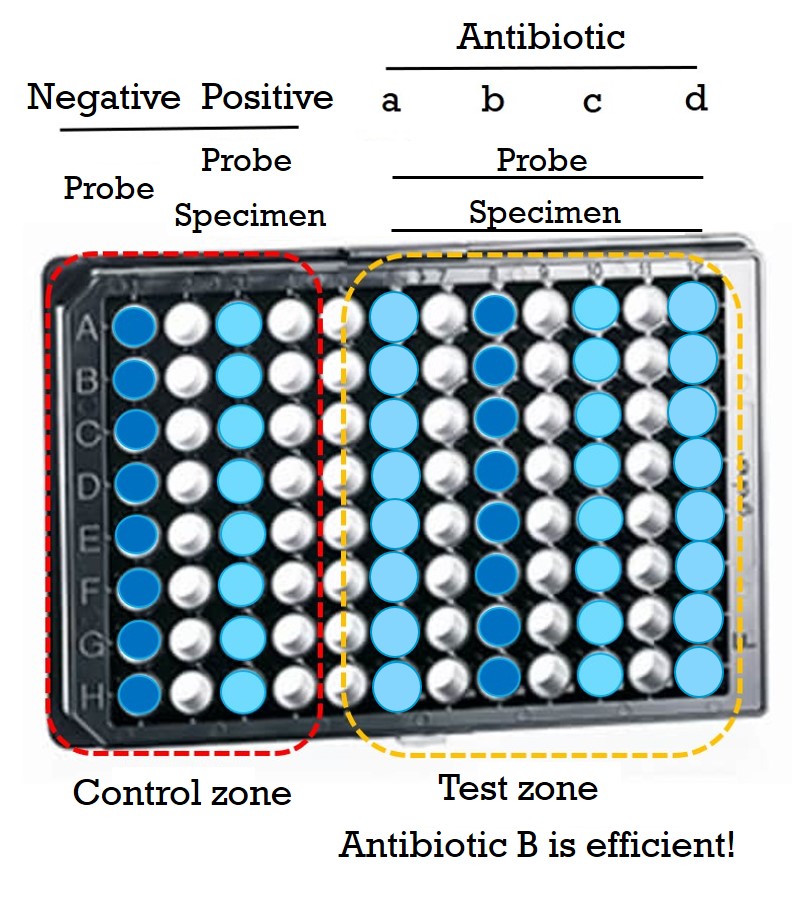
Detection of infectious symptoms takes approximately 3–5 days. This delay may result in missing the golden treatment window, leading to the infection worsening. This technology is the first to utilize biodegradable nanovesicles to encapsulate nanographene, forcing it into an aggregated state that exhibits enhanced fluorescence visible to the naked eye. Additionally, since live bacteria can rapidly degrade these nanovesicles, the encapsulated nanographene is released, transitioning from an aggregated to a non-aggregated state. This transition results in a reduction of fluorescence intensity that is proportional to the bacterial concentration. This technology can be applied in pathogen rapid screening tests, precision medicine, and in vitro diagnostic platforms. Although this method does not identify the bacterial species, it enables the selection of the most suitable antibiotic within just one hour, allowing for timely and effective infection management.
Features / strengths
1. Rapid Analysis: Identifies the most suitable antibiotic within as little as one hour.
2. Easy Operation: Fluorescence changes can be observed directly with the naked eye under a handheld UV lamp.
3. Low Cost: Blue Bubble has low manufacturing costs, and the required detection equipment is inexpensive.
4. Versatile Applications: Applicable to various sample types and clinical settings, as well as basic research and environmental monitoring.
Specification in detail
Blue Bubble
A reagent for detecting pathogen resistance