Introduction
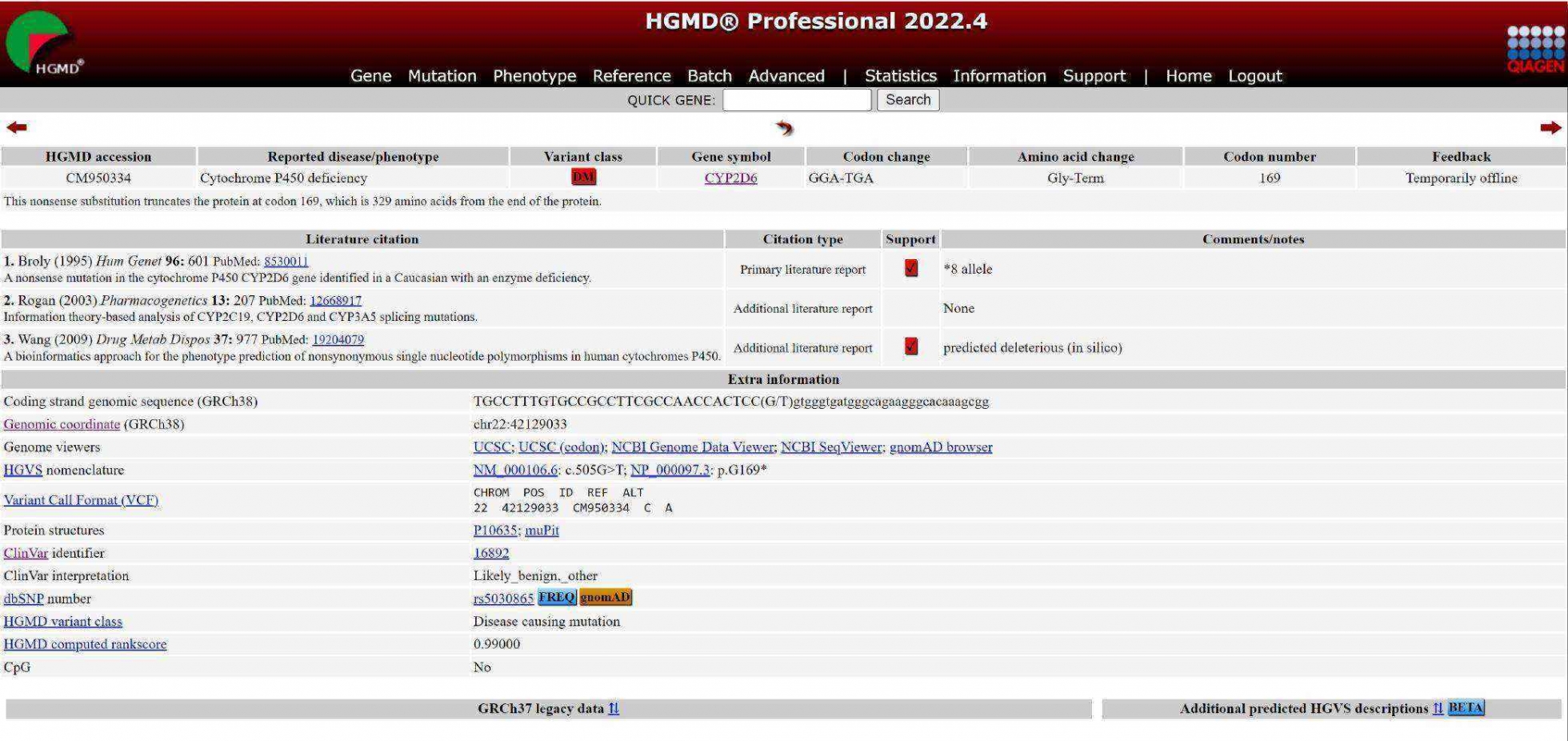
The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) is a comprehensive database that has been collecting and curating information on human genetic disease-related variant loci since 1996. This extensive and continually updated database has been maintained by a genetics team with 12 years of academic experience at Cardiff University in the United Kingdom.
HGMD is considered one of the authoritative databases in the academic community and offers both a professional version and a public version to facilitate research by scientists. Due to the rapid development of high-throughput next-generation sequencing, the rapid accumulation of human mutation locus information has made it increasingly challenging for the public version to meet the needs of clinical research and applications. In comparison to the professional version, the public version is updated only twice a year (compared to every three months with the professional version) and currently contains only 189,186 loci (100,160 loci less than the professional version). In addition to the difference in the number of loci and update frequency, there are also significant differences in function and information presentation between the two versions.
Features / strengths
●Rich genetic information
●Robust search capabilities
●Detailed variant locus information
●Comprehensive classification information
●Comprehensive annotation information
Specification in detail