Introduction
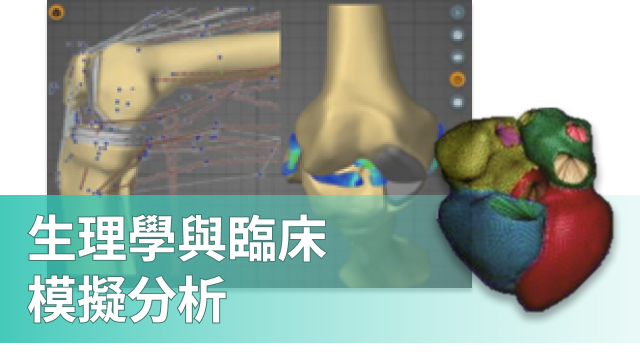
Physiology and Clinical Simulation Solutions are used to simulate human physiology and clinical scenarios to aid in medical research, medical education, and clinical practice. These simulations can be used to study and understand physiological processes, evaluate disease treatment options, train healthcare professionals, and optimize clinical decision-making. Here are some common applications of physiology and clinical simulation solutions:
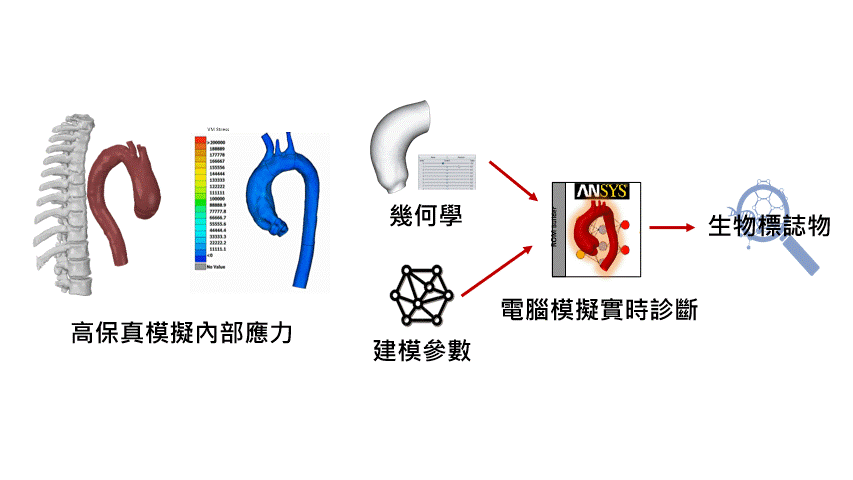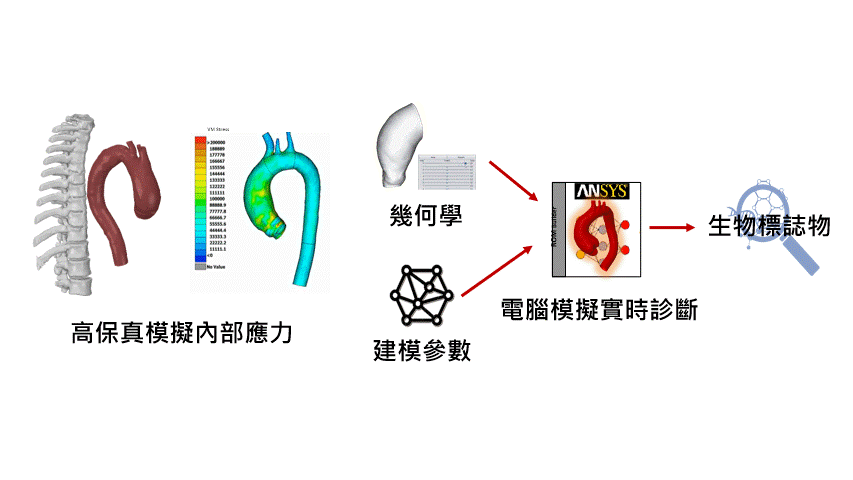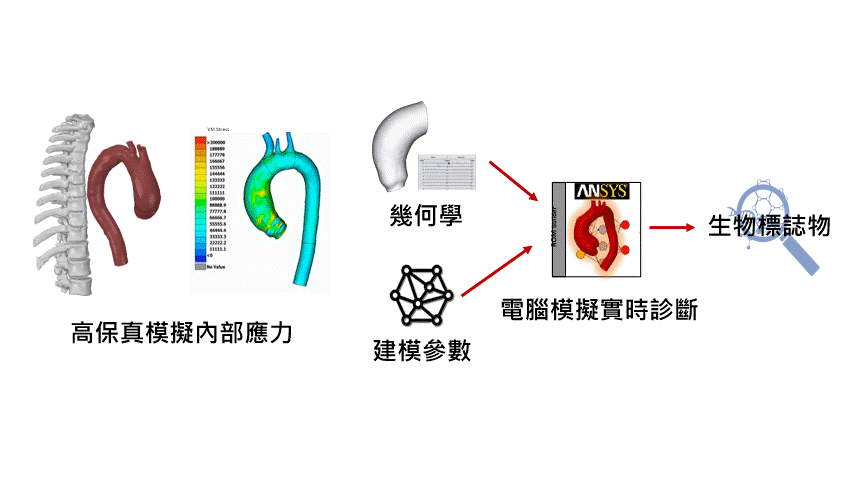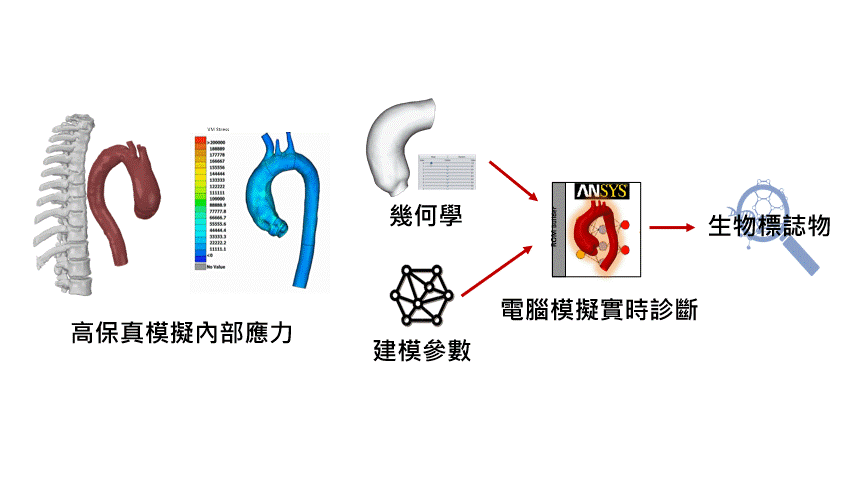
Physiology Research: Physiology simulations can be used to model human physiological processes such as cardiac function, respiratory processes, circulatory systems, neural control, and more. This helps scientists gain a better understanding of physiological phenomena, explore disease mechanisms, and develop new treatment approaches.
Drug Development and Assessment: Physiology simulations can be employed to assess the effectiveness and safety of new drugs. Scientists can use models to predict drug metabolism, absorption, distribution, and elimination, determining optimal dosages and treatment plans.
Clinical Decision Support: Healthcare professionals can use simulations to model the effects of different treatment options, aiding them in making more informed clinical decisions. This is particularly valuable for personalized medicine and patient management.
Medical Education and Training: Physiology and clinical simulations can be used to train medical students, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. Students can practice clinical skills and decision-making through simulated scenarios, enhancing their clinical competence.
Surgical Simulation: In medical training, surgical simulations can help surgeons practice surgical techniques, reducing patient risks. These simulations often include virtual surgeries and hands-on surgical training devices.
Patient Education: Physiology and clinical simulations can also be used for patient education, helping patients better understand their conditions, treatment options, and prognosis.
Studying Individual Variations: Simulations can model different treatment responses based on individual characteristics and physiological conditions, enabling personalized medicine.
By utilizing simulations in medical research, education, and clinical practice, efficiency, safety, and the quality of healthcare can be significantly improved. These simulation techniques not only reduce costs but also enhance standards and practices within the healthcare industry.
Features / strengths
1. Highest Safety: Simulation allows medical professionals to practice and assess different treatment methods in a virtual environment, without exposing patients to risks to their life or health.
2. Customized Treatment: Simulation can simulate treatment outcomes based on individual patient characteristics and physiological conditions, achieving more precise customized treatment.
3. Education and Training: Physiology and clinical simulation provide a safe environment for medical students and healthcare professionals to practice clinical skills, enhance their clinical experience, and improve clinical decision-making abilities.
4. Efficiency and Cost Savings: Simulation can save time and costs by reducing the need for actual clinical internships, while providing more opportunities for practice and assessment.
5. Experimentation and Research: Scientists can use simulation to replicate physiological processes, study disease mechanisms, evaluate new drugs and treatment methods, and optimize medical equipment.
6. Immediate Feedback: Simulation typically provides immediate feedback, enabling students and healthcare professionals to promptly understand the outcomes of their actions and make adjustments and improvements.
7. Treatment Risk Management: In clinical decision support, simulation can assist medical professionals in assessing the risks and benefits of different treatment options, leading to better decision-making for patients.
8. Continuous Enhancement of Treatment Skills: Healthcare professionals can use simulation as part of their ongoing professional development to keep their clinical skills and knowledge up-to-date.
Specification in detail